Ultrasonography
What are the different kinds of ultrasounds?
There are three main categories of ultrasound imaging, including:
- Pregnancy ultrasound (prenatal ultrasound).
- Diagnostic ultrasound.
- Ultrasound guidance for procedures.
how ultrasonography works
Sound Waves: Ultrasonography involves the use of a transducer, which emits high-frequency sound waves. These sound waves are inaudible to the human ear.
Reflection of Sound Waves: When the sound waves encounter different types of tissues or structures inside the body, they are partially reflected back to the transducer.
Image Formation: The transducer picks up the reflected sound waves and converts them into electrical signals. These signals are then processed by a computer to create real-time images or videos of the internal structures.
Visualization of Organs and Structures: Ultrasound can be used to visualize various organs and structures, including the heart, liver, kidneys, uterus, fetus during pregnancy, blood vessels, and more.
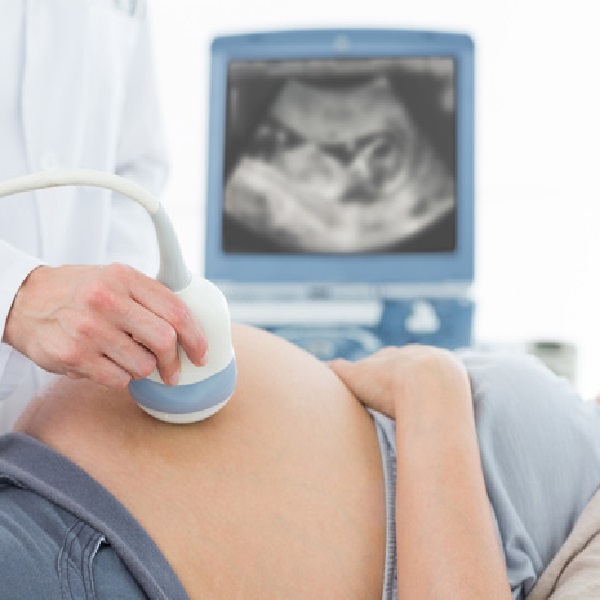
Pregnancy ultrasound
Pregnancy ultrasound, also known as prenatal or obstetric ultrasound, is a medical imaging technique used during pregnancy to visualize and monitor the developing fetus. This non-invasive procedure allows healthcare providers to assess the health and growth of the fetus, confirm the pregnancy, and detect any potential complications.
Here are key aspects of pregnancy ultrasound:
Timing of Ultrasound Examinations:
- Early Pregnancy Ultrasound (First Trimester): Typically performed between 6 and 12 weeks of gestation, this ultrasound confirms the pregnancy, determines the gestational age, and may detect multiple pregnancies.
- Anatomy Scan (Second Trimester): Conducted between 18 and 22 weeks, this detailed ultrasound assesses the fetus’s anatomy, measures growth, and evaluates the placenta and amniotic fluid.
- Third-Trimester Ultrasounds: If necessary, additional ultrasounds may be performed in the third trimester to monitor fetal growth, assess amniotic fluid levels, or address specific concerns.
Types of Pregnancy Ultrasound:
- Transabdominal Ultrasound: A transducer is placed on the abdomen, and a gel is applied to help transmit sound waves through the abdominal wall.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: In early pregnancy, a transducer is inserted into the vagina for a closer view of the uterus and fetus. This method is often used during the first trimester.
Purposes of Pregnancy Ultrasound:
- Confirming Viability: Early ultrasounds confirm the presence of a gestational sac, fetal heartbeat, and viability of the pregnancy.
- Gestational Age Determination: Ultrasound helps estimate the age of the fetus and predict the due date.
- Anatomy Assessment: The mid-pregnancy ultrasound examines the fetus’s organs, limbs, and overall structure to identify any abnormalities.
- Monitoring Growth: Serial ultrasounds in the second and third trimesters track fetal growth, ensuring the baby is developing appropriately.
- Placental and Amniotic Fluid Evaluation: Ultrasound assesses the health and position of the placenta and measures the volume of amniotic fluid.
- Detection of Multiple Pregnancies: Ultrasound is highly effective in identifying twins, triplets, or other multiple pregnancies.
Diagnostic ultrasound
Diagnostic ultrasound, also known simply as medical ultrasound or diagnostic medical sonography, is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of the inside of the body. This imaging modality is widely used for diagnostic purposes in various medical specialties, providing valuable information about the structure and function of organs and tissues.
Here are key aspects of diagnostic ultrasound:
Ultrasound Transducer:
- An ultrasound transducer is a handheld device that emits high-frequency sound waves into the body and receives the echoes produced as the waves bounce back from internal structures.
Sound Wave Propagation:
- The emitted sound waves travel through the body, interacting with different tissues. When the sound waves encounter boundaries between tissues of different densities, some of the waves are reflected back to the transducer.
Image Formation:
- The transducer converts the received echoes into electrical signals, which are processed by a computer to create real-time images or videos displayed on a monitor.
Non-Invasive and Painless:
- One of the key advantages of diagnostic ultrasound is its non-invasive nature. It does not use ionizing radiation, making it safe for routine use, including during pregnancy.
REACH US, WE WILL ASSIST YOU
